Overview of Docker and containers
Regarding this article
Created for in-house young study sessions It explains as easily as possible, understanding the outline, building the environment, and actually operating it.
environment
- Windows 10
- Docker for Windows 2.3.0.4 stable edition
- Authentication proxy exists (items are separated, so if you do not have a proxy, you can skip it)
Overview of Docker and containers
What is a container?
One of the virtualization technologies
What is Docker
One of the container engines shown below
Difference between conventional virtualization (hypervisor type) and container
- Since the container shares the kernel of the host OS, resource usage is low and startup is quick.
- Dependencies can be packaged inside a container
→ Containerized applications can be executed in different environments (portability)
With the conventional hypervisor type, when operating in another environment, it was necessary to obtain materials and manually build the environment.
The story of the OS and the OS kernel
-
OS kernel
-
The one that plays the main role in the OS that mediates between software and hardware.
-
Well-known kernels include Linux and Windows kernels (?)
-
OS
-
Software (UI, drivers, developer tools, etc.) on top of the kernel
-
The Linux kernel is also divided into OSs such as Ubuntu, CentOS, and RHEL depending on the software.

Docker for Windows environment construction
Enable Hyper-V
Since it is necessary to enable Hyper-V to run Docker on Windows, Execute the following command with powershell opened with administrator privileges, Enable Hyper-V (PC restart required)
>Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
After restarting, check if Hyper-V is enabled in BCDEdit *
Execute the following command with powershell,
If it is output by hypervisorlaunchtype Auto, it has been successfully enabled.
- Command line tool for managing boot configuration data (BCD)
bcdedit /enum | find '"hypervisorlaunchtype"'
If it is off, execute the following command and restart again.
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype auto
Installation & setup of docker for windows
Get Docker for Windows (2.3.0.4 stable edition) from the link below https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/
Reboot after installation After restarting, start Docker and the Docker startup procedure will be displayed After the installation is complete, docker for windows will be added to the indicator at the bottom right of the screen
Because it requires a lot of memory to start an image or container Change the memory allocation from 2GB to 4GB from [Setting] → [Resources]
The following is only for those who need proxy authentication
Enter the following settings in [Setting] → [Resources] → [PROXIES].
-Http: //
Why you need Hyper-V (hypervisor) even though it is a container
Hyper-V is a hypervisor, isn't it necessary for containers? You might think This is because the Docker container is based on Linux and requires a Linux kernel. Docker for Windows builds a Linux OS with Hyper-V on Windows OS, The Linux kernel on that Hyper-V is shared by the container
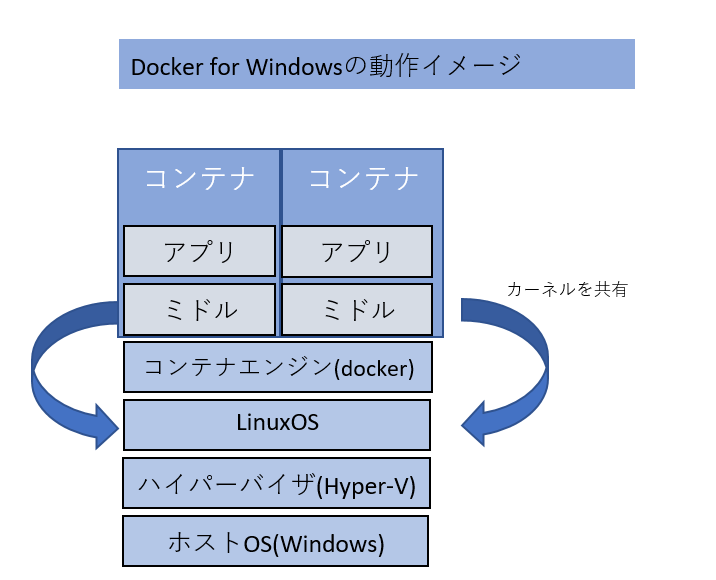
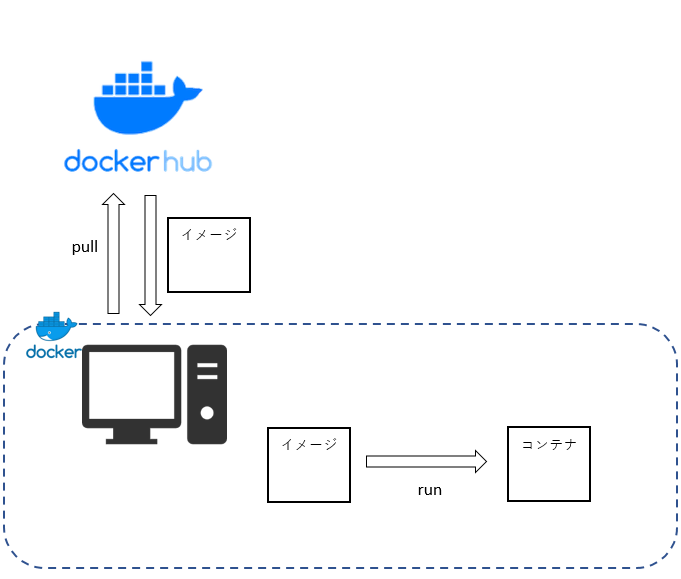
Once you have prepared the operating environment for Docker, you can run your favorite container. Containers can be obtained from a management location on the Internet called Docker Hub (* described later) At this time, the container is distributed in a snapshot-like format called a container image. After acquiring the image, it can be operated as a container by executing it.
Docker operation
DockerHub Container images can be obtained mainly from a management location on the net called Docker Hub Only image search is possible without user registration Here you can check the image name, provider, latest version, etc. https://hub.docker.com/
Get Docker image-Run container
Once you get docker for Windows, you can run docker commands from the command prompt Actually get a lightweight linux image called alpine from docker hub and run it
>docker pull alpine:latest
latest: Pulling from library/alpine
801bfaa63ef2: Pull complete Digest: sha256:3c7497bf0c7af93428242d6176e8f7905f2201d8fc5861f45be7a346b5f23436
Status: Downloaded newer image for alpine:latest
docker.io/library/alpine:latest
>docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
alpine latest 389fef711851 2 weeks ago 5.58MB
>docker run -it -d alpine:latest /bin/sh
>docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c3a9d3cc09f4 alpine:latest "/bin/sh" 6 seconds ago Up 3 seconds loving_mendeleev
docker exec -it c3a9d3cc09f4 /bin/sh
/ # ls
bin dev etc home lib media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
/ # exit
The explanation of each command is as follows
- docker pull
- Getting the image from docker hub
- Specify the image version with a tag, otherwise it will automatically become the latest version
- docker images
- You can check the list of images saved locally
- docker run [optional]
command - Starting the docker image as a container
- By adding the -it option, standard input / output can be performed in the container.
- You can also specify the command to move at login with the command.
- In/bin/sh, you can start a shell, access docker, and then enter commands.
- -d specifies to start in the background
- docker ps
- Get a list of running containers
- docker exec [optional]
command - Go inside the running container
- You can exit the container with exit
Dockerfile
When actually creating a container, in addition to the base image Often create a container with the necessary middleware and apps It is possible to operate inside the started container, When you create a configuration as a Dockerfile, You will be able to set up and copy resources automatically
Launching a web server container using Dockerfile
Here is an example of creating a simple web server container
Dockerfile
#Use image of web server nginx
#Pull the image specified here from docker hub
FROM nginx:alpine
#You can copy materials from a local terminal to a container environment with ADD
#/usr/share/nginx/html is the place to store html to be displayed by nginx
ADD ./index.html /usr/share/nginx/html
#Free up 80 ports in the container
EXPOSE 80
#Set the entry point for the container
ENTRYPOINT /usr/sbin/nginx -g "daemon off;" -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
index.html
hello world,Docker
After creating the above file, execute the following command in the saved directory
Working folder/◀ Start command prompt here ├ Dockerfile └index.html
>docker build -t myimage .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 4.096kB
Step 1/5 : FROM nginx:alpine
---> 629df02b47c8
Step 2/5 : CMD echo "now running..."
---> Using cache
---> 2b4f225ff66e
Step 3/5 : ADD ./index.html /usr/share/nginx/html
---> Using cache
---> 8de80809c52c
Step 4/5 : EXPOSE 80
---> Using cache
---> 90168e587d3b
Step 5/5 : ENTRYPOINT /usr/sbin/nginx -g "daemon off;" -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
---> Running in eb60ad7be198
Removing intermediate container eb60ad7be198
---> d4d131ab1d24
Successfully built d4d131ab1d24
Successfully tagged myimage:latest
>docker run --name mycontainer -d -p 30080:80 myimage
- docker build -t
path - Generate an image based on the contents of Dockerfile
- -t is an option to name the image you create
- Image name can be set freely
- In the path, specify the path of the Dockerfile used for build
- Since it is saved in the current this time, specify [.]
- docker run --name
-d -p 30080: 80 - Create a container based on the image name
- --name is an option to name the container
- -p is a setting that exposes the container port to the host
- Release 80 ports of the container with Dockerfile,
- Connecting to port 30080 on the host will connect to port 80 on the container After starting the container, when I tried to access it, the web server was started and the html created earlier was displayed.
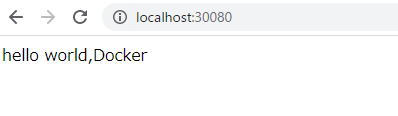
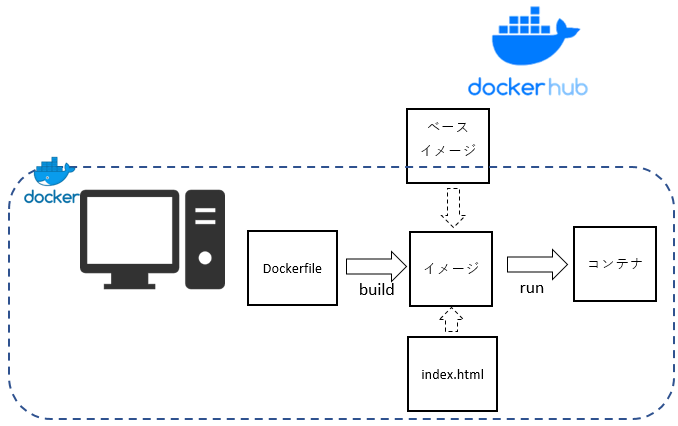
Impressions of actually using the container
Because the project I currently belong to uses various technologies It was difficult to build the environment one by one, but when using Docker, If you generate a Dockerfile and put it in the source repository I find it very useful because each member can create a container environment and move their hands. Actually, I use a technology called docker-compose that can set up multiple containers. I'm exhausted so please refer to another article Also, when it comes to actual operation, it is essential to use orchestration tools such as k8s. I thought that this level of knowledge was sufficient for light movements such as feasibility studies.
Recommended Posts