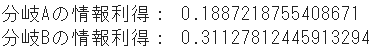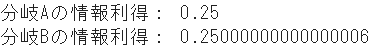- Für den Entscheidungsbaum gibt es mehrere Klassifizierungskriterien.
- Häufig werden zwei Verunreinigungsmessungen verwendet, Gini-Verunreinigungen und Entropie sowie ein Teilungskriterium, das als Fehlklassifizierungsfehler bezeichnet wird.
- Sehen wir uns diese Unterschiede an.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
Vergleich jedes Index in 2 Klassenklassifikationen
- Wenn in der 2-Klassen-Klassifizierung das Verhältnis einer Klasse p ist, wird jeder Index wie folgt berechnet.
- ** Gini: $ 2p * (1-p) $ **
- ** Entropie: $ -p * \ log p- (1-p) * log (1-p) $ **
- ** Fehlklassifizierungsrate: $ 1-max (p, 1-p) $ **
#Generieren Sie eine Gleichheitssequenz entsprechend p
xx = np.linspace(0, 1, 50) #Startwert 0, Endwert 1, Anzahl der Elemente 50
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
#Berechnen Sie jeden Index
gini = [2 * x * (1-x) for x in xx]
entropy = [-x * np.log2(x) - (1-x) * np.log2(1-x) for x in xx]
misclass = [1 - max(x, 1-x) for x in xx]
#Grafik anzeigen
plt.plot(xx, gini, label='gini', lw=3, color='b')
plt.plot(xx, entropy, label='entropy', lw=3, color='r')
plt.plot(xx, misclass, label='misclass', lw=3, color='g')
plt.xlabel('p', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('criterion', fontsize=15)
plt.legend(fontsize=15)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.grid()
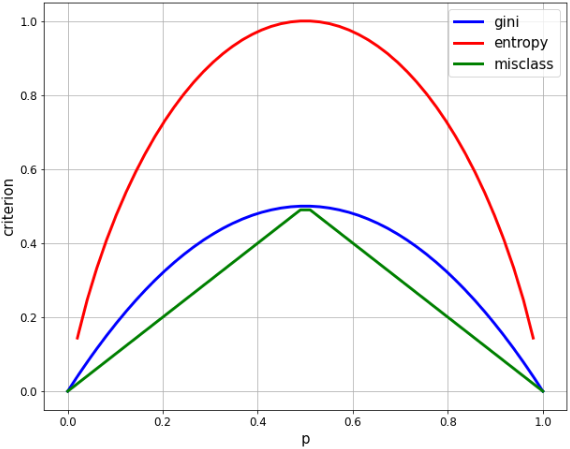
- Wenn das Verhältnis von 2 Klassen gleich ist (p = 0,5), sind beide die Maximalwerte,
- Die maximale Entropie beträgt 1,0 und die Gini beträgt 0,5. Skalieren Sie die Entropie daher zum einfachen Vergleich um den Faktor 1/2.
#Generieren Sie eine Gleichheitssequenz entsprechend p
xx = np.linspace(0, 1, 50) #Startwert 0, Endwert 1, Anzahl der Elemente 50
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
#Berechnen Sie jeden Index
gini = [2 * x * (1-x) for x in xx]
entropy = [(x * np.log((1-x)/x) - np.log(1-x)) / (np.log(2)) for x in xx]
entropy_scaled = [(x * np.log((1-x)/x) - np.log(1-x)) / (2*np.log(2)) for x in xx]
misclass = [1 - max(x, 1-x) for x in xx]
#Grafik anzeigen
plt.plot(xx, gini, label='gini', lw=3, color='b')
plt.plot(xx, entropy, label='entropy', lw=3, color='r', linestyle='dashed')
plt.plot(xx, entropy_scaled, label='entropy(scaled)', lw=3, color='r')
plt.plot(xx, misclass, label='misclass', lw=3, color='g')
plt.xlabel('p', fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('criterion', fontsize=15)
plt.legend(fontsize=15)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.grid()
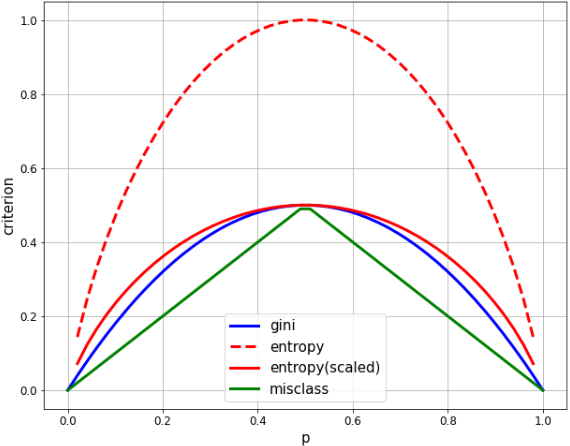
- Gini und Entropie sind sehr ähnlich, beide zeichnen eine quadratische Kurve und maximieren bei p = 1/2.
- Die Fehlklasse unterscheidet sich deutlich darin, dass sie linear ist, aber viele der gleichen Eigenschaften aufweist. Es maximiert bei p = 1/2, ist bei p = 0, 1 gleich Null und ändert sich in einem Berg.
Unterschiede in jedem Index im Informationsgewinn
1. Was ist Informationsgewinn?
- ** Informationsgewinn ** ist ein Index, der angibt, um wie viel die Unreinheit vor und nach der ** Teilung abgenommen hat, als Daten unter Verwendung einer bestimmten Variablen geteilt wurden.
- Je weniger unrein, desto nützlicher ist die Variable als Klassifizierungsbedingung.
- In diesem Sinne ist das Reduzieren der Reinheit gleichbedeutend mit ** Maximieren des Informationsgewinns in jedem Zweig **.
- Für die Klassifizierung in zwei Klassen wird ** Informationsgewinn (IG) ** in der folgenden Formel definiert.
- \displaystyle IG(D_{p}, a) = I(D_{p}) - \frac{N_{left}}{N} I(D_{left}) - \frac{N_{right}}{N} I(D_{right})
- $ I $ bedeutet unrein, $ D_ {p} $ sind die Daten des übergeordneten Knotens, links und rechts von den Daten des untergeordneten Knotens sind $ D_ {left} $ und $ D_ {right} $ und der übergeordnete Knoten Das linke und rechte Verhältnis der untergeordneten Knoten basiert auf der Anzahl der Knotenabtastungen $ N $ als Nenner.
2. Berechnen Sie den Informationsgewinn für jeden Index
- Nehmen Sie die folgenden zwei Verzweigungsbedingungen A und B an.
- Vergleichen Sie den Informationsgewinn zwischen den Verzweigungsbedingungen A und B für jede der Gini-, Entropie- und Fehlklassifizierungsraten.
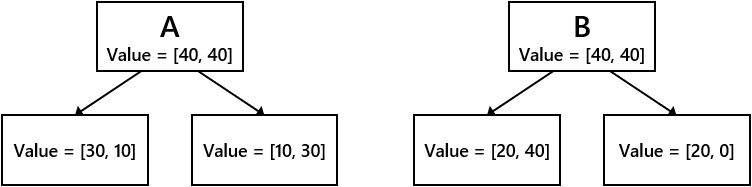
➀ Informationsgewinn durch Gini unrein
#Gini-Reinheit des Elternknotens
IGg_p = 2 * 1/2 * (1-(1/2))
#Gini-Reinheit des untergeordneten Knotens A.
IGg_A_l = 2 * 3/4 * (1-(3/4)) #links
IGg_A_r = 2 * 1/4 * (1-(1/4)) #richtig
#Gini-Unreinheit des Kinderknotens B.
IGg_B_l = 2 * 2/6 * (1-(2/6)) #links
IGg_B_r = 2 * 2/2 * (1-(2/2)) #richtig
#Informationsgewinn jeder Branche
IG_gini_A = IGg_p - 4/8 * IGg_A_l - 4/8 * IGg_A_r
IG_gini_B = IGg_p - 6/8 * IGg_B_l - 2/8 * IGg_B_r
print("Informationsgewinn von Zweig A:", IG_gini_A)
print("Informationsgewinn von Zweig B:", IG_gini_B)

➁ Informationsgewinn durch Entropie
#Übergeordnete Knotenentropie
IGe_p = (4/8 * np.log((1-4/8)/(4/8)) - np.log(1-4/8)) / (np.log(2))
#Entropie des untergeordneten Knotens A.
IGe_A_l = (3/4 * np.log((1-3/4)/(3/4)) - np.log(1-3/4)) / (np.log(2)) #links
IGe_A_r = (1/4 * np.log((1-1/4)/(1/4)) - np.log(1-1/4)) / (np.log(2)) #richtig
#Entropie des untergeordneten Knotens B.
IGe_B_l = (2/6 * np.log((1-2/6)/(2/6)) - np.log(1-2/6)) / (np.log(2)) #links
IGe_B_r = (2/2 * np.log((1-2/2+1e-7)/(2/2)) - np.log(1-2/2+1e-7)) / (np.log(2)) #richtig,+1e-7 fügt einen kleinen Wert hinzu, um eine 0-Division zu vermeiden
#Informationsgewinn jeder Branche
IG_entropy_A = IGe_p - 4/8 * IGe_A_l - 4/8 * IGe_A_r
IG_entropy_B = IGe_p - 6/8 * IGe_B_l - 2/8 * IGe_B_r
print("Informationsgewinn von Zweig A:", IG_entropy_A)
print("Informationsgewinn von Zweig B:", IG_entropy_B)
➂ Informationsgewinn aufgrund von Fehlklassifizierungsraten
#Fehlklassifizierungsrate des übergeordneten Knotens
IGm_p = 1 - np.maximum(4/8, 1-4/8)
#Fehlklassifizierungsrate des untergeordneten Knotens A.
IGm_A_l = 1 - np.maximum(3/4, 1-3/4) #links
IGm_A_r = 1 - np.maximum(1/4, 1-1/4) #richtig
#Fehlklassifizierungsrate des untergeordneten Knotens B.
IGm_B_l = 1 - np.maximum(2/6, 1-2/6) #links
IGm_B_r = 1 - np.maximum(2/2, 1-2/2) #richtig
#Informationsgewinn jeder Branche
IG_misclass_A = IGm_p - 4/8 * IGm_A_l - 4/8 * IGm_A_r
IG_misclass_B = IGm_p - 6/8 * IGm_B_l - 2/8 * IGm_B_r
print("Informationsgewinn von Zweig A:", IG_misclass_A)
print("Informationsgewinn von Zweig B:", IG_misclass_B)
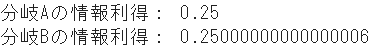
Zusammenfassung
|
Klassifizierungsbedingung A. |
Klassifizierungsbedingung B. |
| Gini unrein |
0.125 |
0.167 |
| Entropie |
0.189 |
0.311 |
| Fehlklassifizierungsrate |
0.250 |
0.250 |
- Es ist klar, dass die Klassifizierungsbedingung B sowohl bei Gini als auch bei Entropy Vorrang hat. In der Tat werden die Ergebnisse sehr ähnlich sein.
- Andererseits sind die Klassifizierungsbedingungen A und B in der Fehlklassifizierungsrate nahezu gleich.
- Auf diese Weise besteht bei der Fehlklassifizierungsrate in der Regel kein eindeutiger Unterschied zwischen Variablen. Im Entscheidungsbaummodell von sklearn gibt es also zwei Teilungskriterien (wie es scheint): Gini und Entropie.
- Außerdem ist Gini möglicherweise etwas schneller, da es keine logarithmische Berechnung wie Entropie gibt.