[PYTHON] Calcul du courant dans le circuit électrique CC
Qu'est-ce que c'est
J'ai fait de Python le code C # qui calcule le courant du circuit électrique que j'ai fait il y a longtemps. J'utilise [la loi de Kirchhof](https://ja.wikipedia.org/wiki/ Loi de Kirchhoff (circuit électrique)).
Code Python
import networkx as nx
import pandas as pd
from more_itertools import pairwise
class CycleInfo:
"""Informations sur le cycle"""
def __init__(self, g, i, cycle):
"""g.Ajouter un index aux cids des arêtes"""
self.cycle = cycle
self.volt = self.resist = self.cur = 0
for e in pairwise(cycle + [cycle[0]]):
if dc := g.edges.get(e):
coe = 1
else:
coe, dc = -1, g.edges[e[1], e[0]]
self.volt += coe * dc['volt']
self.resist += dc['resist']
dc['cids'].append((coe, i))
def calc_current(df):
"""Calcul actuel. Le résultat est ajouté à la colonne cur"""
g = nx.DiGraph()
for row in df.itertuples():
g.add_edge(row.node1, row.node2, volt=row.volt,
resist=row.resist, cids=[])
cycles = nx.cycle_basis(g.to_undirected())
cinfos = [CycleInfo(g, i, cycle) for i, cycle in enumerate(cycles)]
vv = [[0] * len(cinfos) for _ in cinfos] #Quantité d'influence
from itertools import combinations
for dc in g.edges.values():
for (coe1, cid1), (coe2, cid2) in combinations(dc['cids'], 2):
vv[cid1][cid2] += -coe1 * coe2 * dc['resist']
vv[cid2][cid1] += -coe1 * coe2 * dc['resist']
modified = True
while modified:
modified = False
for i, cinfo in enumerate(cinfos):
if not cinfo.resist:
if not cinfo.volt:
continue
raise ValueError('Court-circuit')
cur = cinfo.volt / cinfo.resist
dif = cur - cinfo.cur
if abs(dif) < 1e-8:
continue
modified = True
cinfo.cur = cur
for j, cinfo2 in enumerate(cinfos):
cinfo2.volt += dif * vv[i][j]
df['cur'] = [sum(cinfos[i].cur for _, i in dc['cids'])
for _, dc in g.edges.items()]
return df
Échantillon 1
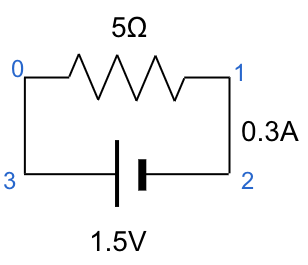
circ1.csv
node1,node2,volt,resist
0,1,0,5
1,2,0,0
2,3,1.5,0
3,0,0,0
Résultat d'exécution (colonne cur)
df = pd.read_csv('circ1.csv')
calc_current(df)
| node1 | node2 | volt | resist | cur | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0.3 |
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 2 | 2 | 3 | 1.5 | 0 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 |
Échantillon 2

circ2.csv
node1,node2,volt,resist
0,1,0,20
0,2,0,10
1,2,0,20
1,3,0,50
2,3,0,40
3,4,0,0
4,5,30,0.98
5,0,0,0
Résultat d'exécution (colonne cur)
df = pd.read_csv('circ2.csv')
calc_current(df)
| node1 | node2 | volt | resist | cur | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 20 | 0.372554 |
| 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 10 | 0.509811 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 20 | -0.0588243 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 50 | 0.431378 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 40 | 0.568635 |
| 5 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.00001 |
| 6 | 4 | 5 | 30 | 0.98 | 1.00001 |
| 7 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.00001 |